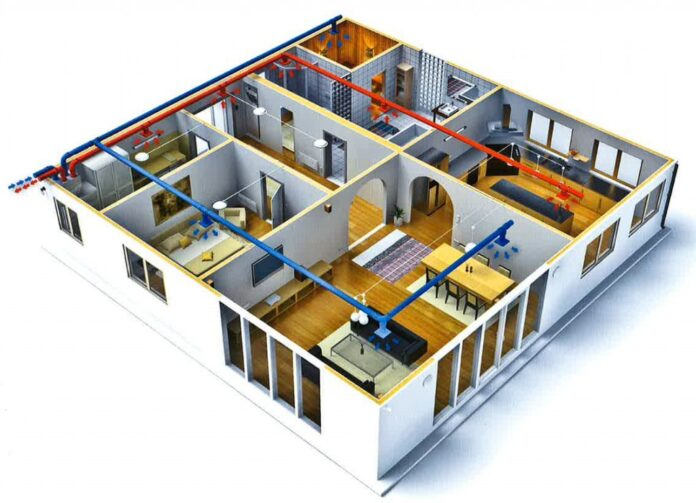
Mechanical ventilation plays a crucial role in maintaining indoor air quality and comfort in modern buildings. Whether it’s a residential home, office building, or healthcare facility, proper ventilation is essential for the health and well-being of occupants. In this ultimate guide to mechanical-ventilation, all the important facts and information will be covered to help you understand the importance of this system in today’s buildings.
The Vital Role of Mechanical-Ventilation in Modern Buildings
In contemporary architecture, mechanical-ventilation emerges as a cornerstone of environmental control, playing a pivotal role in ensuring the sanctity of indoor spaces. This system, dedicated to the expulsion of stale air and the introduction of fresh external air, is indispensable in safeguarding the health and comfort of building occupants. The mechanism behind mechanical-ventilation is adept at balancing indoor air quality by mitigating pollutants, odours, and excessive humidity.
These functions are particularly crucial in densely populated or heavily used buildings where natural ventilation may fall short of maintaining optimal air conditions. The strategic removal of harmful gases, such as carbon dioxide, by mechanical-ventilation systems, underscores their importance in preventing the deterioration of indoor air quality which could otherwise culminate in adverse health outcomes for individuals within these spaces.
Furthermore, these systems play a critical role in circumventing the accumulation of moisture, thereby averting the growth of mould and mildew which are known to contribute to respiratory issues and allergic reactions. By ensuring a consistent and controlled exchange of air, mechanical-ventilation supports a healthy and productive environment, free from the detriments of air stagnation. This is especially significant in environments like healthcare facilities, where the purity of air is paramount, and in office buildings, where the wellbeing of employees directly influences productivity.
Ventilation Requirements in Different Building Types
The ventilation needs of buildings vary greatly depending on their use, size, and the activities conducted within. Here’s a brief overview of the key ventilation requirements for different types of buildings:
Residential Homes
- Continuous background ventilation to remove pollutants from cooking, cleaning, and occupancy.
- Enhanced ventilation in kitchens and bathrooms to control humidity and odours.
- Provision for purge ventilation through windows or higher capacity fans for rapid air quality improvement.
Office Buildings
- Demand-controlled ventilation to adjust air supply based on occupancy levels, reducing energy consumption during off-peak hours.
- Zoning systems to accommodate different ventilation needs in various areas (e.g., meeting rooms vs open-plan offices).
- Filtration systems to minimise outdoor pollutants entering the workspace, especially in urban areas.
Healthcare Facilities
- High-efficiency particulate air (HEPA) filtration to prevent the spread of infections.
- Separate ventilation systems for different zones to avoid cross-contamination between general areas, operating theatres, and isolation rooms.
- Controlled humidity levels to maintain a sterile environment and prevent the growth of mould and bacteria.
Educational Institutions
- Adequate ventilation in classrooms to enhance cognitive performance and reduce the transmission of airborne diseases.
- Systems that ensure minimal disruption from noise for a conducive learning environment.
- Sports facilities and laboratories require specialised ventilation to manage higher levels of humidity and control hazardous fumes.
Industrial and Manufacturing Facilities
- Robust systems to extract harmful emissions and provide fresh air, crucial for worker safety and comfort.
- Tailored solutions for areas with heat-generating equipment to control temperature and ensure equipment efficiency.
- Explosion-proof ventilation in sections dealing with flammable materials or chemicals.
Each building type requires a unique approach to ventilation to meet specific health, safety, and comfort standards. Engaging with mechanical-ventilation professionals ensures that these needs are met effectively, tailored to the unique characteristics and functions of the building.
Installation Considerations for Mechanical-Ventilation
When embarking on the installation of mechanical-ventilation systems, several pivotal considerations come to the forefront. Among these, the dimension and configuration of the edifice play a significant role in dictating the appropriate scale and type of system required. It is imperative that the chosen setup adequately caters to the spatial dimensions, ensuring a uniform distribution of air across all zones within the premises.
The architectural layout further influences the strategic positioning of air intake and exhaust portals. An optimal location ensures that the intake of air is from areas with lower pollution levels, whilst exhaust vents are placed to effectively dispel air away from the building, thereby preventing re-entry of contaminated air.
Collaboration with seasoned professionals who specialise in the field of mechanical-ventilation is crucial. These experts bring a wealth of knowledge and experience, essential for designing a system that not only aligns with the specific needs of the building but also adheres to prevailing regulations and standards. Their expertise ensures the system’s capacity to efficiently manage air quality, temperature, and humidity levels, contributing to a salubrious indoor environment.
 The Relationship between Energy Efficiency and Mechanical Ventilation
The Relationship between Energy Efficiency and Mechanical Ventilation
In the contemporary landscape of building design, the synergy between mechanical ventilation and energy efficiency emerges as a crucial consideration. Mechanical-ventilation systems, by their nature, are pivotal in maintaining ambient indoor air quality. However, their operational dynamics possess the potential to significantly influence a building’s energy consumption profile. The strategic implementation of energy-efficient ventilation technologies not only embodies a commitment to environmental stewardship but also ensures a reduction in operational costs.
The introduction of heat recovery systems exemplifies a forward-thinking approach to enhancing energy efficiency within mechanical-ventilation frameworks. These systems adeptly reclaim energy from exhaust air, repurposing it to temper incoming fresh air, thereby reducing the demand on heating and cooling systems. Such innovation underscores the feasibility of achieving optimal indoor air quality without incurring a substantial energy penalty.
Similarly, the adoption of demand-controlled ventilation presents an intelligent method of aligning ventilation rates with occupancy levels. By modulating air flow based on actual need, these systems significantly curtail energy consumption, negating the inefficiencies associated with static ventilation rates. This responsive approach to ventilation not only ensures the well-being of occupants but also aligns with the broader objectives of energy conservation and sustainability.
Common Challenges and Solutions in Mechanical-Ventilation
In the operation of mechanical-ventilation systems, several challenges may arise, impacting their efficiency and effectiveness. One frequent issue is the occurrence of uneven airflow, which can lead to certain areas within a building not receiving adequate ventilation. This problem often stems from incorrect system design or installation errors. To mitigate this, a comprehensive review of the system’s layout and adjustment of ductwork or fan speeds may be required.
Another common challenge is the presence of high levels of pollutants despite the ventilation system being operational. This can occur if the system’s filters are not capturing contaminants effectively, or if the air intake is positioned in a polluted external environment. Addressing this involves the regular replacement or upgrading of filters to higher efficiency models and re-evaluating the positioning of air intakes to ensure they draw in cleaner air.
Mechanical-ventilation systems may also face issues related to excessive noise, which can be disruptive for occupants. This often results from fan or ductwork vibrations or from airflow turbulence. Solutions include installing sound dampening materials, ensuring that components are securely fastened, and using low-noise fans.
Maintenance Tips for Optimal Performance of Mechanical-Ventilation
Ensuring the optimal performance of mechanical-ventilation systems is essential for maintaining indoor air quality and efficiency. Here are some maintenance tips:
Regular Inspection and Cleaning
Schedule routine inspections and cleaning of the entire ventilation system, including ductwork, fans, and filters, to prevent dust and debris accumulation which can impair system efficiency.
Filter Replacement
Change or clean air filters regularly, according to the manufacturer’s recommendations or more frequently in environments with high levels of pollutants, to ensure effective air filtration and maintain air flow.
Check for Duct Leakage
Inspect ductwork periodically for any signs of leakage, which can significantly reduce system efficiency. Seal any leaks with appropriate materials to ensure optimal performance.
Fan Maintenance
Ensure that fan blades are clean and free of debris, as dirt on fan blades can reduce efficiency. Check fan motors and bearings for signs of wear and lubricate as needed to prevent failure.
Monitor System Performance
Keep an eye on the system’s performance, including airflow rates and humidity levels. Any sudden changes may indicate a problem that requires attention.
Control System Updates
For systems with automated controls, ensure that the software is kept up-to-date. Outdated control systems can lead to inefficiencies and increased energy consumption.
Professional Audit
Engage a professional to conduct an annual audit of the system. They can identify any inefficiencies or potential issues that may not be obvious to a layperson and suggest corrective actions.
Educate Occupants
Where applicable, educate building occupants about the proper use of the ventilation system, including the importance of keeping vents clear of obstructions and the benefits of maintaining a consistent setting.
By adhering to these maintenance tips, the longevity and efficiency of mechanical-ventilation systems can be significantly enhanced, contributing to a healthier indoor environment and potentially reducing energy costs.
The Future of Mechanical-Ventilation Technologies
The horizon for mechanical-ventilation technologies is characterised by a rapid pace of innovation, promising to redefine the landscape of indoor air management. Emerging trends focus on the integration of artificial intelligence and Internet of Things (IoT) capabilities, which are set to offer unprecedented levels of efficiency and user-friendliness. These smart systems, through the utilisation of sensors and automated controls, can dynamically adjust ventilation rates in response to real-time indoor air quality data and occupancy patterns, thus achieving optimal environmental conditions with minimal energy expenditure.
Energy-efficient components are also at the forefront of this evolution, with developments in low-power consumption fans and advanced heat recovery units making significant strides. These innovations not only reduce the operational costs associated with mechanical-ventilation but also align with global sustainability goals by minimising carbon footprints.
Moreover, the advent of integrated building management systems heralds a new era in which mechanical-ventilation is part of a holistic approach to building operations. These systems enable a seamless coordination between ventilation, heating, and air conditioning units, ensuring that each operates at peak efficiency and in harmony with the others. This integration facilitates a comprehensive view of a building’s environmental controls, allowing for more sophisticated management strategies that can adapt to changing conditions and requirements.
Conclusion
In wrapping up this comprehensive exploration of mechanical ventilation, it’s clear that the significance of these systems in modern architecture cannot be overstated. The journey through the multifaceted roles of mechanical-ventilation has illuminated its indispensable contribution to maintaining indoor air quality, ensuring occupant comfort, and enhancing energy efficiency in buildings of diverse typologies.
FAQs
What differentiates mechanical ventilation from natural ventilation?
Mechanical ventilation utilise fans and ductwork to control the flow of air within buildings, providing a consistent and regulated environment regardless of external conditions. In contrast, natural ventilation relies on passive air flow through windows, doors, and vents without the aid of mechanical systems, making it less controllable and often ineffective in tightly sealed buildings or extreme weather conditions.
How often should filters in a mechanical-ventilation system be replaced or cleaned?
The frequency of filter maintenance in mechanical-ventilation systems can vary depending on several factors including the type of system, the specific filters used, and the level of pollutants in the environment. Generally, it is advised to inspect filters every 3 to 6 months and replace or clean them as necessary to ensure optimal air quality and system efficiency.
Can mechanical-ventilation systems help reduce energy costs in buildings?
Yes, modern mechanical-ventilation systems, especially those equipped with heat recovery technologies and demand-controlled ventilation can significantly reduce energy consumption. By recovering heat from exhaust air and adjusting ventilation rates based on occupancy and indoor air quality, these systems can lower the need for additional heating or cooling, thus reducing overall energy costs.
Are mechanical-ventilation systems suitable for all types of buildings?
Mechanical-ventilation systems can be designed and tailored to suit a wide range of buildings, from residential homes to commercial spaces and specialised facilities like hospitals. The key is to engage with professionals in mechanical-ventilation to ensure that the system is appropriately sized and configured to meet the specific requirements of the building, taking into account factors such as occupancy, building layout, and local climate conditions.
| Other Good Articles to Read |
| Blogs-Nation |
| Blogs-Peoples |
| Bryan Smith Blogs |
| intellect blogs |
| the fault in our blogs |
| blogs eu |
| oz forums |
| recruitment blogs |
| zet blogs |
| id blogs |
| Blog Studio legale |
| blogs map |
| Related Business Listings |
| Contact Directory |
| Local Business Profiles |